
(Z)-endoxifen for Duchenne
Advancing a Potential New Approach for Boys Living With DMD
Atossa Therapeutics is initiating a new research and development program to explore its investigational oral therapy, endoxifen, as a potential treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
DMD is a serious, progressive neuromuscular disease that primarily affects boys, leading to loss of muscle function, loss of ambulation, and life-threatening heart and respiratory complications. Despite important advances, there remains a significant need for therapies that can be used broadly across the DMD community.
Our goal is to evaluate whether endoxifen’s unique biology may offer a new, mutation-independent treatment strategy for people living with DMD.

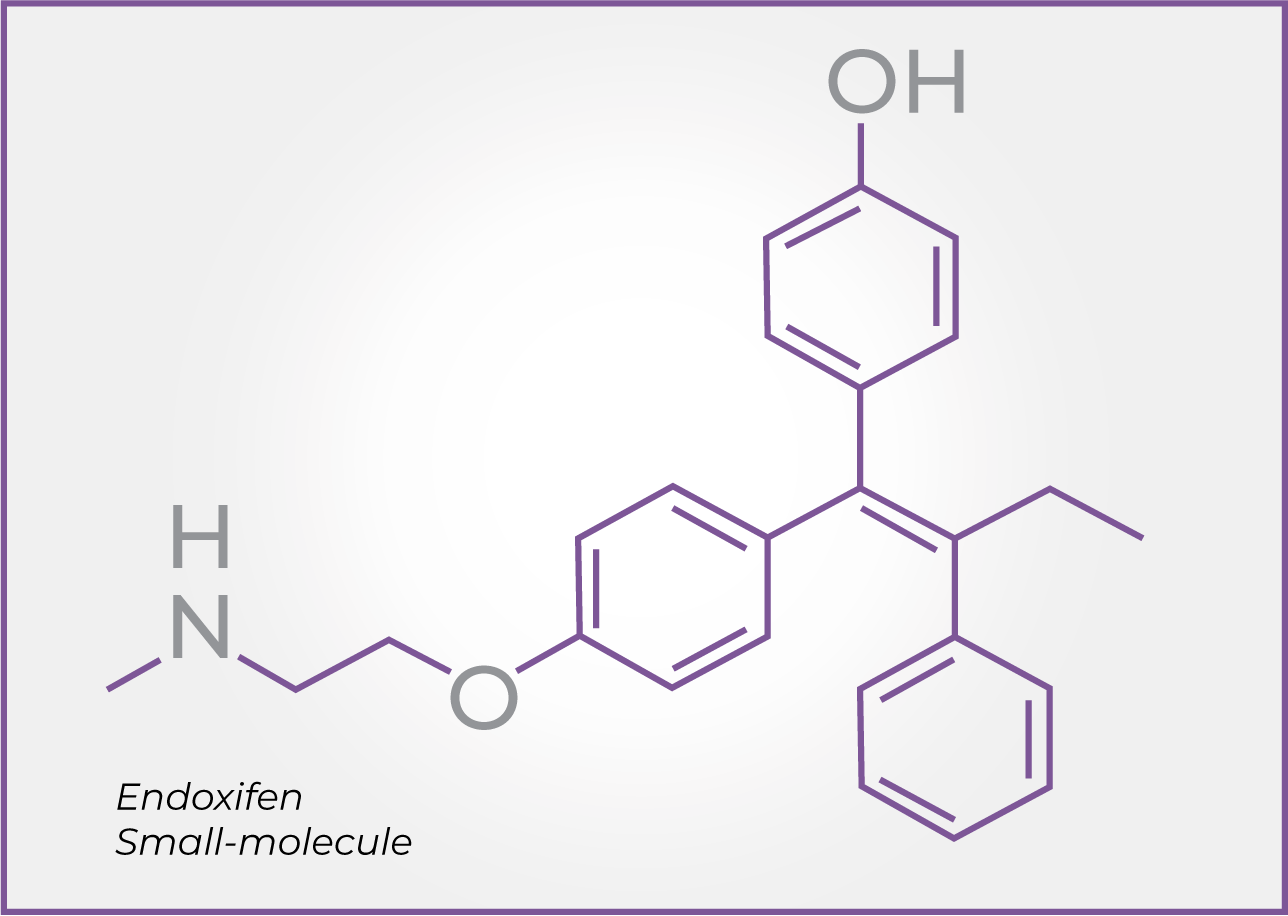
(Z)-endoxifen
What Is Endoxifen?
Endoxifen is an investigational small-molecule therapy and a major active metabolite of tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that has been widely used in other indications.
Because endoxifen directly engages estrogen receptors, it has the potential to modulate pathways involved in muscle health, including muscle growth, repair, and fibrosis. Atossa is developing an oral formulation of endoxifen designed to achieve consistent drug exposure and enable convenient, once-daily dosing, subject to ongoing development and evaluation.
Endoxifen is not approved for use in DMD or any muscular dystrophy indication. Its safety and efficacy for these uses have not been established.
Understanding Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
DMD is a rare, genetic, X-linked disorder caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, which is essential for maintaining the structure and stability of muscle cells. Without functional dystrophin, muscle fibers are easily damaged and progressively replaced by fat and fibrotic tissue.
Children with DMD typically:
- Show symptoms in early childhood, such as delayed motor milestones and difficulty running or climbing
- Lose the ability to walk in their early teens, on average
- May develop serious cardiac and respiratory complications as the disease progresses
While several therapies have been approved for certain subgroups of patients, no current treatment is curative, and many boys and young men with DMD still face a substantial disease burden.
LEARN MORE at CureDuchenne.org

Infographic ©2025 CureDuchenne
Why Endoxifen in DMD? – Scientific Rationale
Skeletal muscle is responsive to hormonal signaling, including estrogen receptor pathways, which can influence:
- Muscle regeneration and repair
- Inflammation and oxidative stress
- Fibrosis and tissue remodeling
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) have shown biological activity in muscle and are being explored in various neuromuscular contexts. As a potent, active metabolite, endoxifen may offer:
- Direct estrogen receptor modulation in muscle tissue
- Oral dosing potential, supporting chronic administration if ultimately proven safe and effective
- A mutation-independent mechanism, meaning it could, in principle, be studied across the broader DMD population, regardless of the underlying dystrophin gene mutation
Atossa’s program is designed to rigorously evaluate this scientific rationale through preclinical and, if appropriate, future clinical studies.
Unmet Need and Treatment Landscape
Current DMD management typically involves:
- Corticosteroids, which can help slow disease progression but are associated with significant side effects
- Mutation-specific therapies, such as exon-skipping or gene-targeted approaches, which are available only to patients with certain genetic variants
- Supportive care, including cardiac and respiratory management, physical therapy, and orthopedics
There is a clear need for additional, generally applicable treatment options that could be used alone or alongside existing therapies. A mutation-agnostic, orally administered therapy—if shown to be safe and effective—could potentially reach a broad range of individuals with DMD.
Atossa’s Endoxifen–DMD Program
Atossa is in the early stages of developing endoxifen for DMD. The program is focused on:
- Preclinical evaluation of endoxifen in models relevant to DMD and muscle biology
- Characterizing pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics to better understand dosing and exposure
- Assessing safety in nonclinical studies to support potential future clinical development
Pending the results of these studies and applicable regulatory feedback, Atossa may advance endoxifen into clinical trials in patients with DMD to evaluate safety, tolerability, and exploratory measures of efficacy.
Because this is an investigational program, there is currently no guarantee that endoxifen will demonstrate benefit in DMD or obtain regulatory approval.
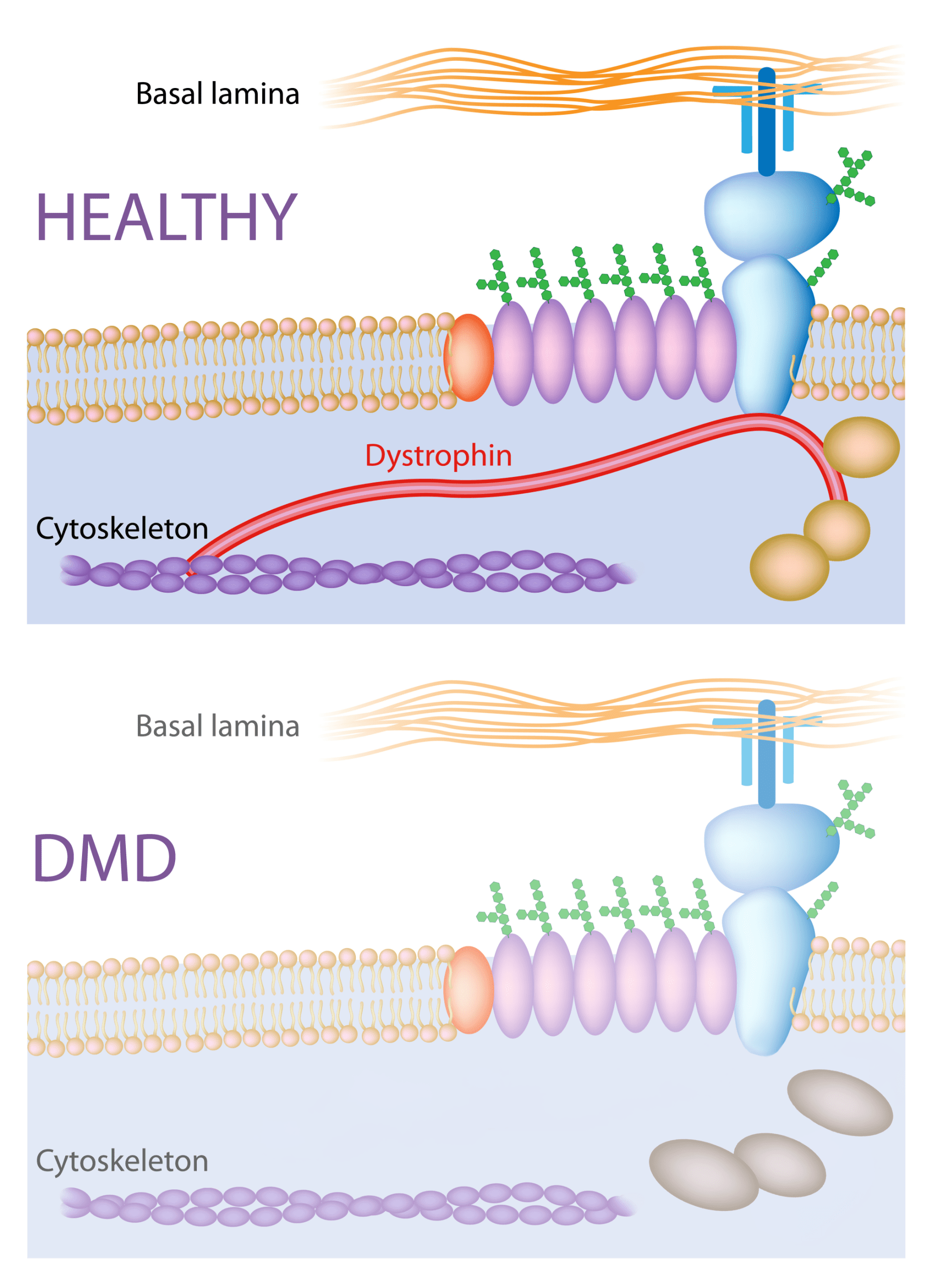
Dystrophin-related protein complex in healthy muscle versus muscle affected by Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Our Commitment to the DMD Community
Atossa is committed to developing innovative therapies for serious conditions where patients have limited options. In DMD, this means:
- Listening to patients and families to understand their needs and priorities
- Collaborating with clinicians, researchers, and advocacy organizations to design thoughtful studies
- Pursuing rigorous science and transparent communication as the program progresses
We recognize the urgency felt by families affected by DMD and are dedicated to advancing our research as responsibly and efficiently as possible.
Stay Informed
As the endoxifen–DMD program advances, Atossa plans to share updates through:
- Company press releases and news updates
- Scientific and medical conference presentations
- Future communications tailored to the DMD community
For media, medical, or collaboration inquiries, please contact:
pr@atossatherapeutics.com
(212) 655-0924
To receive updates on Atossa’s development programs, including our work in DMD, please sign up for email alerts or visit our News & Events page.
Endoxifen is an investigational agent. It has not been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or any other regulatory authority for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy or any other muscular dystrophy indication. Safety and efficacy have not been established.


